Syphilis is an STD infection caused due to the bacteria Treponema pallidum. It has 3 main stages through which a person infected with syphilis goes if the disease advances. If left untreated can lead to even life-threatening complications.
Formation of gummas is one such complication, which is in the third stage of syphilis, wherein soft, tumor-like growths can affect the skin, bones, and internal organs.
In this blog, we see the causes of gumma syphilis, exploring its etiology, symptoms, pictures of gumma syphilis, diagnosis, and available treatments.
Causes of Gumma Syphilis
Gumma is a granulomatous lesion that develops during tertiary syphilis. Gummas form during the tertiary phase of syphilis, this is the late stage of the disease. When Syphilis remains untreated for a very long period of time, the immune system comes into act against the Syphilis bacteria (Treponema pallidum) leading to inflammation and damage of tissues. This process results in the formation of granulomatous lesions known as gummas.
The exact mechanism of gumma development is not fully understood. Still, it is believed by experts that it may be a result of delayed hypersensitivity reactions to the presence of Treponema pallidum bacteria and its component.
The response of the immune system may have also resulted in the accumulation of immune cells and fibrous tissues, causing the peculiar nodular appearance of gummas.
Identifying Symptoms of Gumma Syphilis
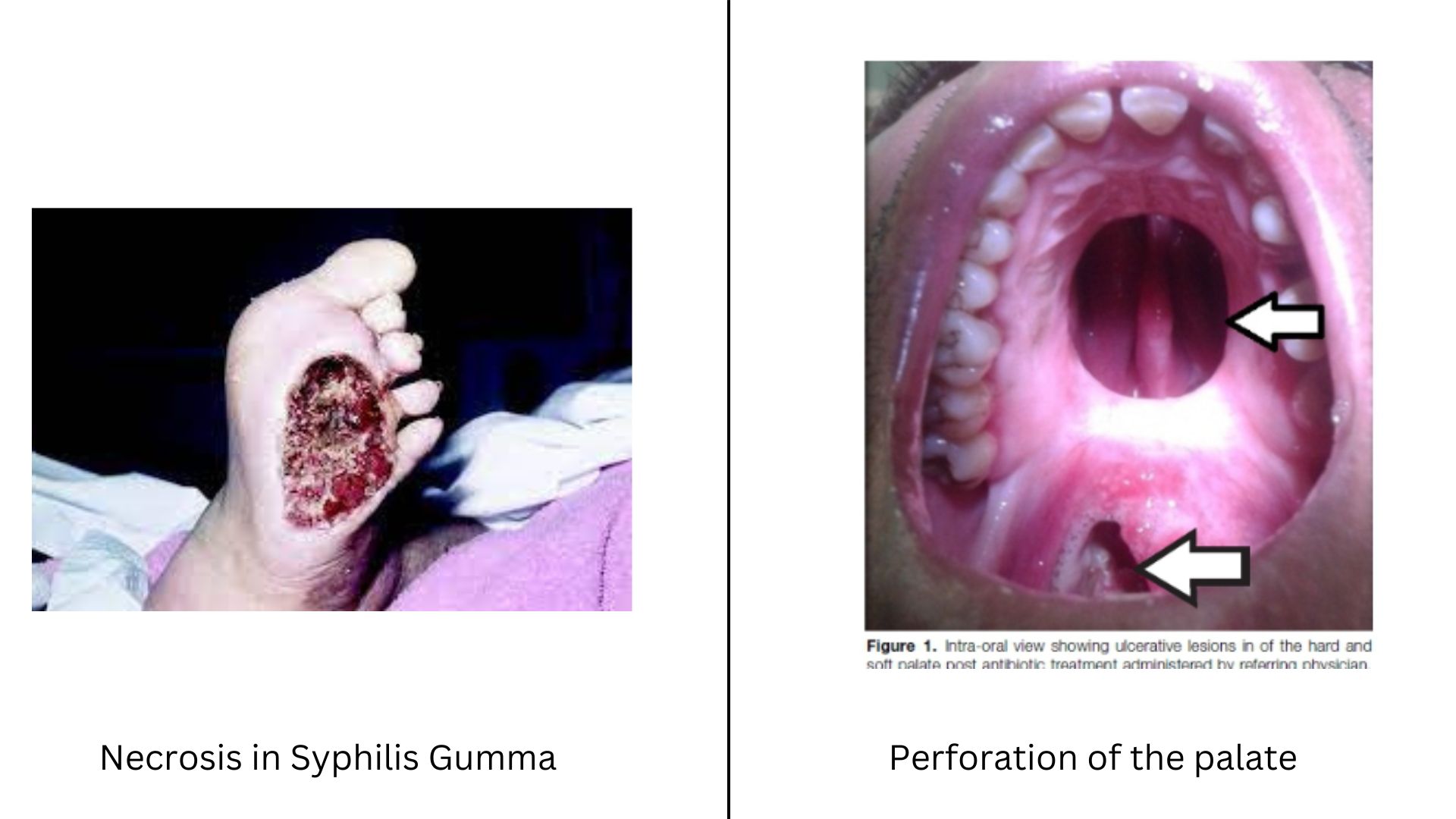
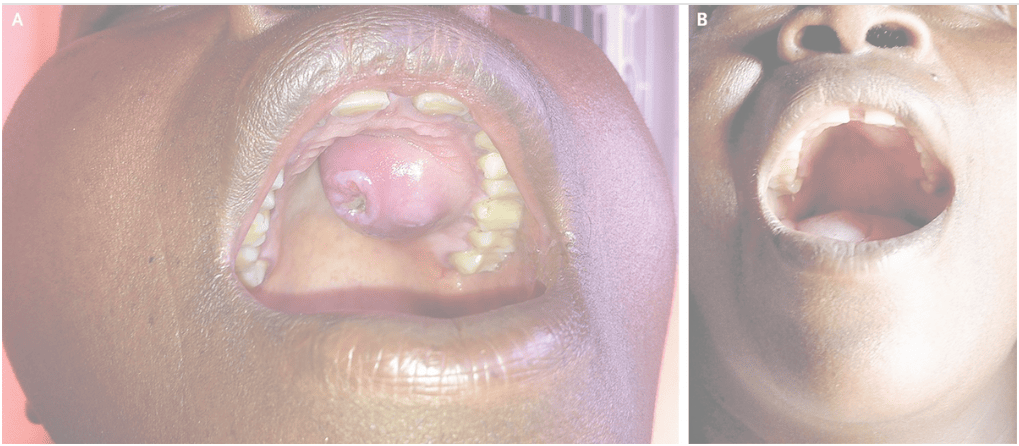
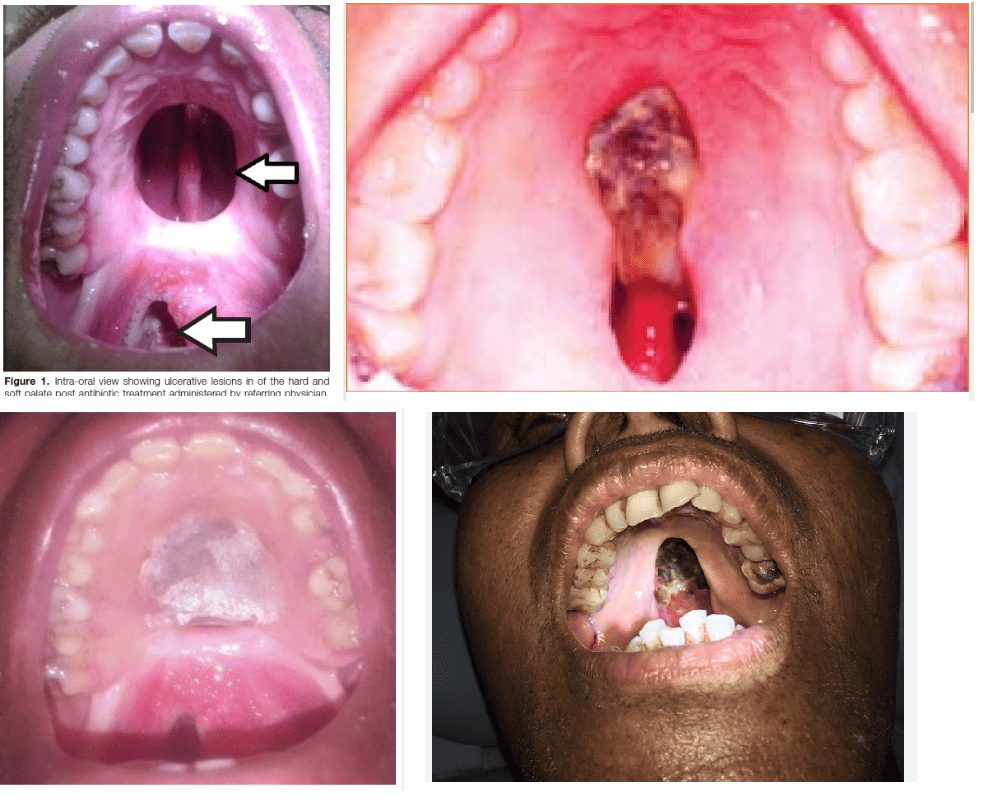
Gummas can appear on different parts of the body, and the symptoms may vary as per their location. Syphilis Gummas mainly affect the skin, bones, liver, and nervous system. However, the place where syphilis gummas can be observed or seen is on the skin and the gamma that appears on the palate, which is on the roof of the mouth and may affect tongue.
Note: Gumma on the Bone, Liver or Brain is not easily citable by physical observation and thus requires clinical diagnosis.
Types of Syphilis Gummas
A syphilitic gumma is a manifestation of tertiary syphilis, which is the advanced stage of syphilis. Gumma can develop in various tissues of the body. In the context of syphilis, gumma typically forms within organs or tissues such as the skin, bones, brain liver, heart, and other organs. At different organs it is known by a different name, a few of which are as follows.
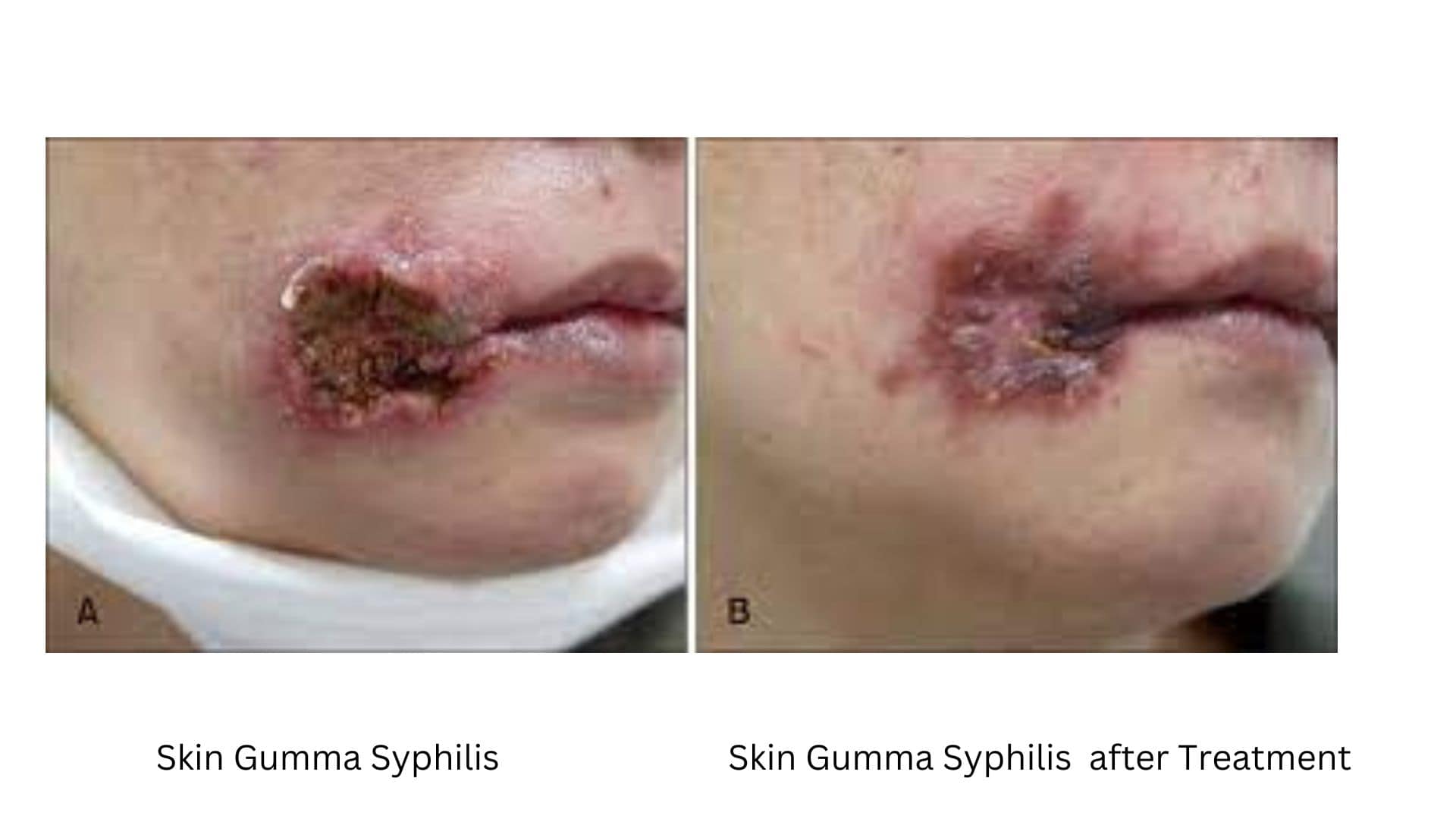
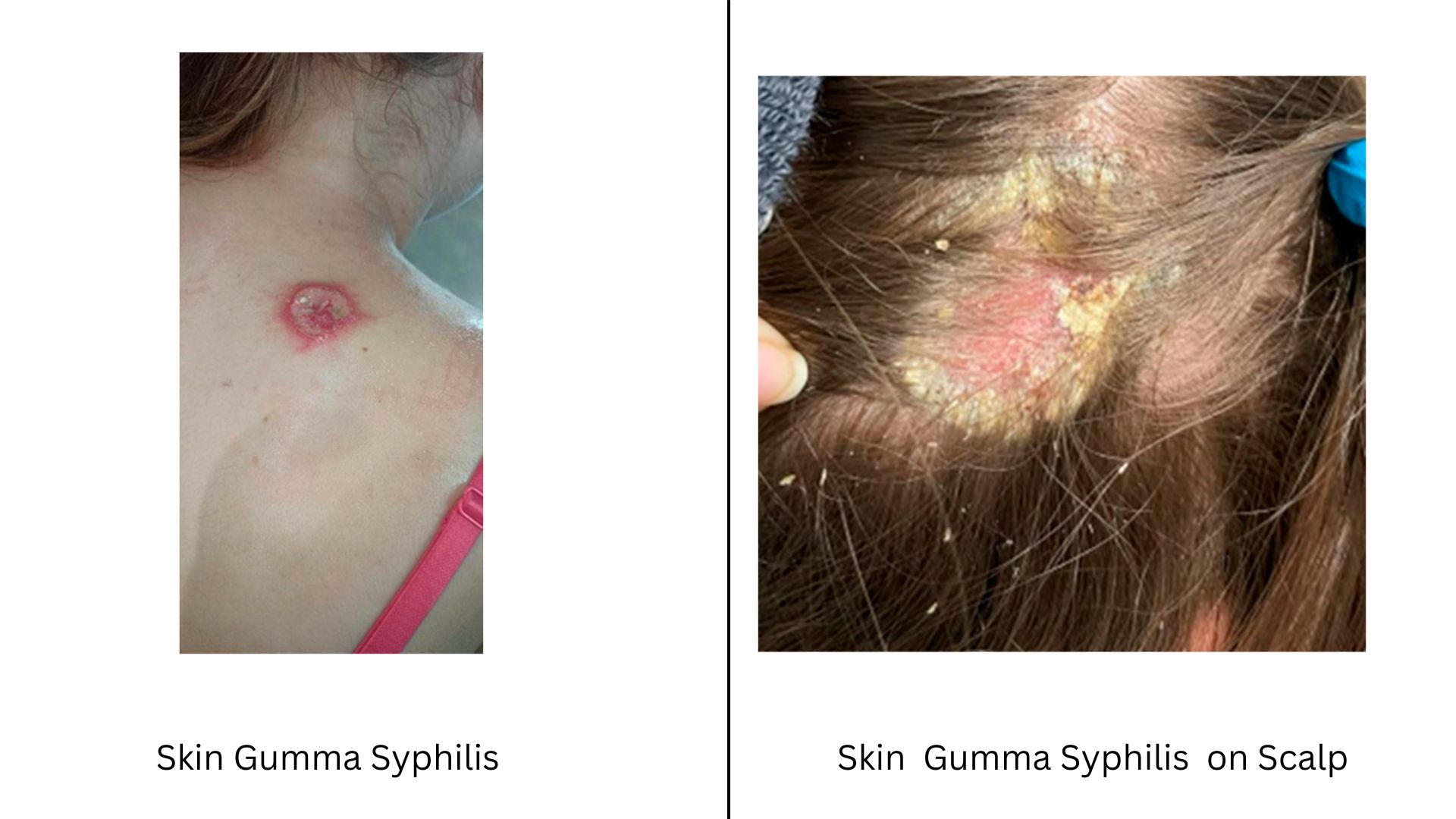
Cutaneous Gummas or Gummas of Skin
In simple terms, this is gumma of skin, which affects the skin and can appear as nodules or ulcers.
Common characteristics of cutaneous gummas include:
- Non-tender Nodules: They usually appear as painless nodules under the skin. They appear to be a rubber-like nodule beneath the skin and in some cases it is movable.
- Ulceration: In the next stage, central necrosis can be seen in the picture below
This means the death of a cell inside the human body, which results in ulceration with a necrotic base. This is the stage where the ulceration starts gathering pace as they become slow to heal and can be prone to secondary bacterial infections.
Color and Size: Gummas comes in different size and some may grow big to several centimeters in diameter while their color ranges from pink to reddish-brown or violaceous.
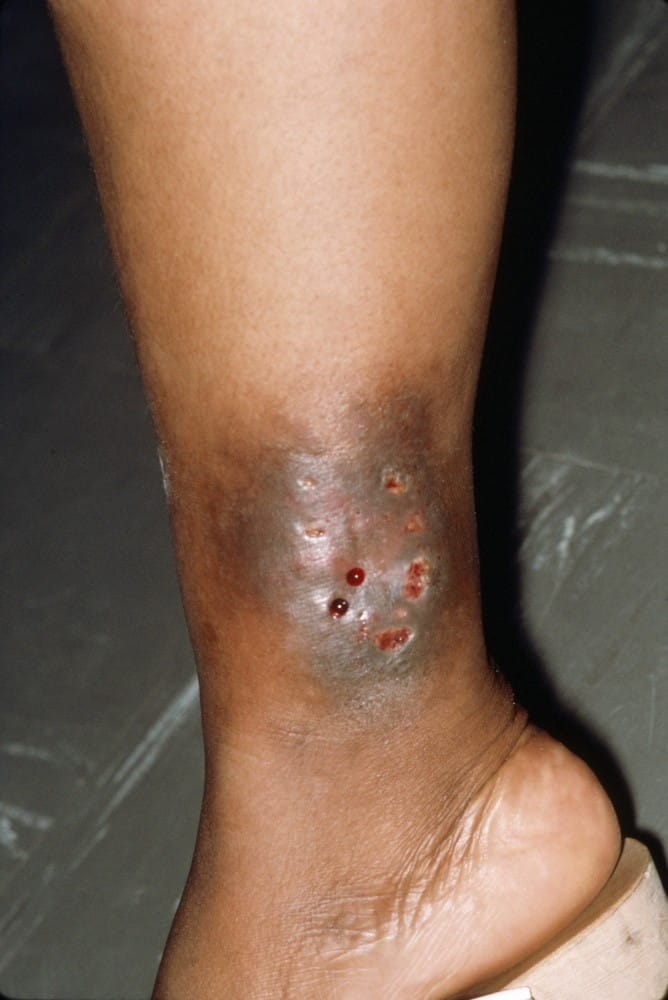
Location: Cutaneous type gummas can come on any part of the body but are commonly found in areas that have had previous injuries or trauma, such as the lower extremities.
Osseous Gummas or Gummas related to bones
Osseous Gumma is related to bone so they can appear in different ways depending on their location and to the extent of bone involvement.
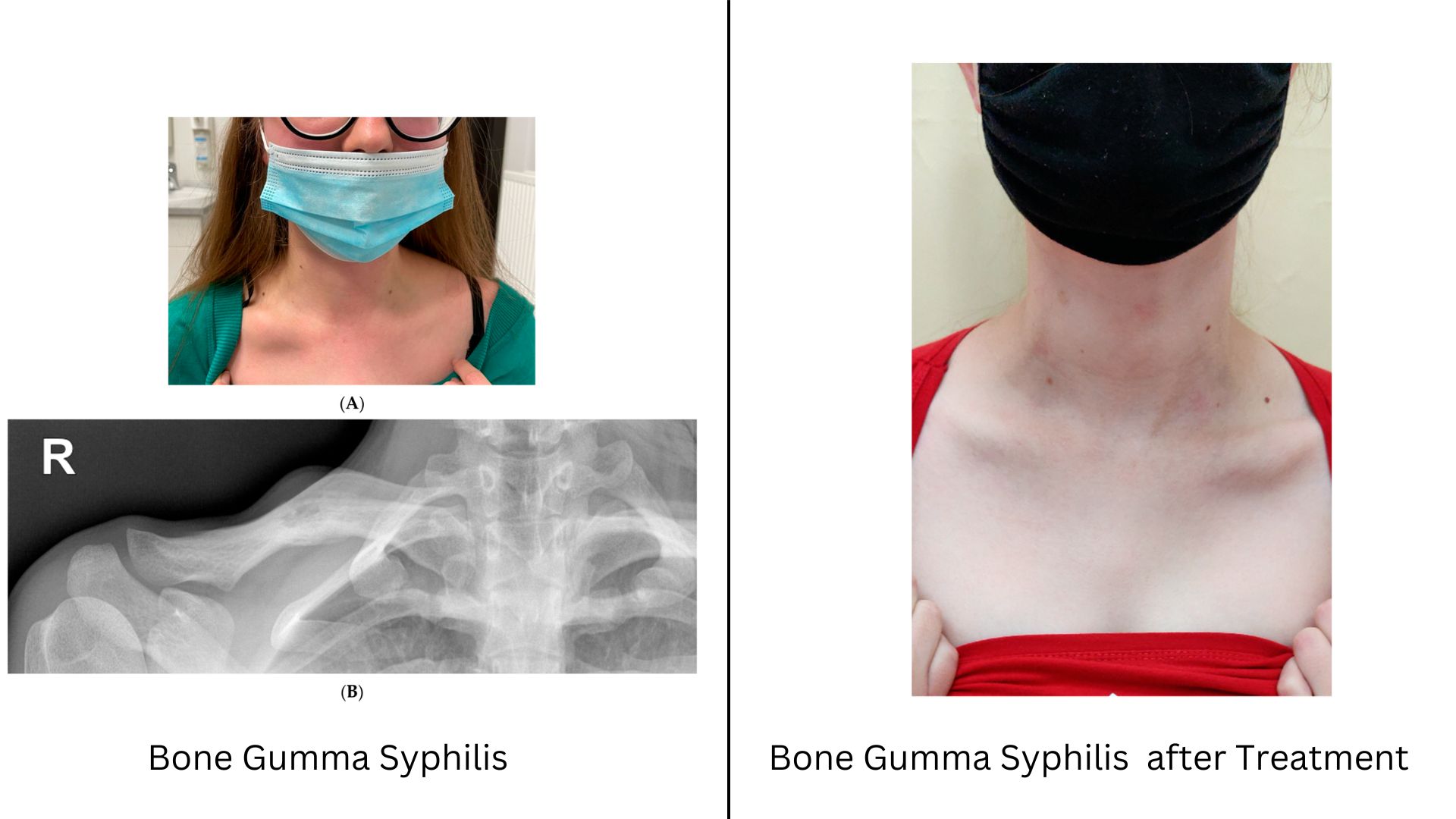
Common characteristics of osseous gummas may include:
Bone Pain: Bone pain is the most common symptom of Osseous gummas. In the initial stage, the pain may be dull, but it is localized to the affected bone before it starts aching or throbbing in the later stage.
Bone deformation: As the gumma progresses, it can cause swelling in the affected bone area which can lead to deformation over time, altering the bone structure and shape.
In some cases, osseous may affect the adjacent joint bones leading to joint pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
In many cases, it was observed that the weakened bone structure has resulted in an increasing risk of fracture of the affected part
Hepatic Gumma or Liver Gumma
Hepatic gumma can appear in a variety of ways on the body, which can range from asymptomatic to severe. Some of the common clinical presentations of hepatic gummas include:
Hepatomegaly: Swelling or enlarged liver is the typical characteristic of hepatic gummas (also known as hepatomegaly). During physical diagnosis, a doctor may feel tenderness in place of the liver which can be palpated below the ribcage on the right side of the abdomen.
Liver Dysfunction: In the later stage as hepatic gummas advance further, they can disrupt normal liver function. This may lead to diseases such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, nausea, and disturbances in the level of enzymes in blood tests.
Stomach Ache: Some individuals with hepatic gummas may experience abdominal pain or discomfort, which can be localized to the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
Neurological Gumma or Brain Gumma
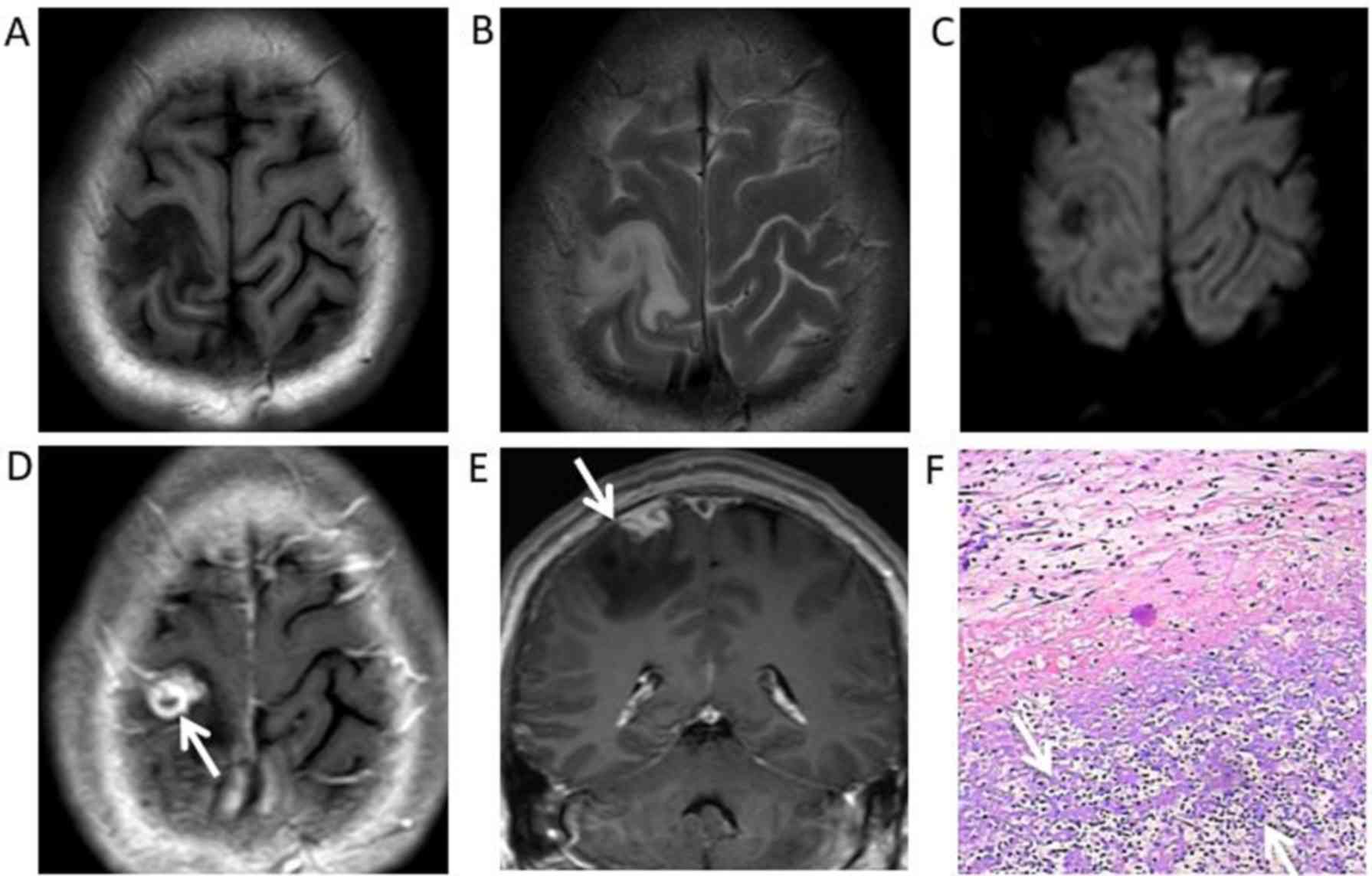
Symptoms of Neurological Gummas can have a wide range of clinical features, depending on the location of the granulomas within the nervous system. Some of the common clinical presentations of neurological gummas include:
Neurological Deficits: People with neurological gumma can find difficulty coordinating movements (ataxia), weakness, sensory disturbances, and cranial nerve abnormalities.
Visual Changes: In case of damage caused to the cranial nerve a person may experience vision changes, such as blurred vision, visual field defects, or even complete vision loss.
Headaches: Chronic or recurrent headaches may occur due to the physical inflammation and pressure caused by neurological gummas.
Seizures: In very rare cases, neurological gummas may damage the brain tissue, leading to seizures.
Cognitive Decline: A person may experience personality changes and memory problems, and cognitive decline is observed in areas of the brain involved in these functions.
Treatment Options for Gumma Syphilis
The treatment of gumma syphilis involves the intake of antibiotics to eradicate the underlying infection.
- Penicillin is usually used for treating syphilis, including gummas. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment depend on the stage and severity of the infection.
- Alternative antibiotics like doxycycline or ceftriaxone may be considered for patients who are allergic to penicillin.
However, it’s essential to follow up or visit the doctor’s office to get it treated by a qualified healthcare professional and to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. In cases where gummas have caused significant damage to organs or tissues, additional medical interventions, such as surgery, may be necessary to address the complications.
Prevention of Syphilis Gumma
Preventing gumma syphilis begins with practicing for prevention of Syphilis. Having safe sex and getting regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections is also a part of prevention.
Early detection and treatment of syphilis during its inception stage or secondary stages can prevent the development of gummas and other complications associated with late-stage syphilis (tertiary syphilis).
Public health efforts also play a crucial role in raising awareness about syphilis, promoting safe sex practices, and providing accessible testing and treatment services.
Education campaigns targeting both the general population and healthcare professionals are essential for reducing the incidence of syphilis and its complications.
Conclusion
Gumma syphilis is a serious manifestation of late-stage syphilis, characterized by the formation of soft, tumor-like growths that can affect various organs and tissues. Early detection and prompt treatment of syphilis during its primary and secondary stages are essential to prevent the development of gummas and other complications associated with tertiary syphilis. If you suspect you may have syphilis or have been exposed to the infection, seek medical attention immediately for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Remember, knowledge and awareness are powerful tools in the fight against syphilis and its devastating consequences.
“
References
Perforation of the palate – A report of two Syphilitic Gumma cases: http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0011-85162020000600008
Gumma Syphilis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syphilis