Human papillomaviruses also called HPVs make up a group of over a hundred related viruses that infect people.Yearly, around 12,000 women living in the US get diagnosed with cervical cancer and more than 3000 lose their life, even with testing and treatment.
HPV can affect you in two types by cause two types of reactions 1) Low-risk HPV: Common skin condition 2) Genital HPV
Most HPV is can cause common skin warts usually on the hands or feet. However about 40 types of HPV infect the genitals which are the sex organs on the outside of the body. These HPV s cause the most common sexually transmitted infections illnesses transmitted from one person to another through sexual activity. Types of cancers caused by HPV include cervical and cancers including that of the vulva, vagina, penis, or anus.
Some genital HPV warts are low risk and may only cause warts on and around the genitals and anus of both women and men.
Rarely this HPV s can also cause warts inside the mouth and throat.
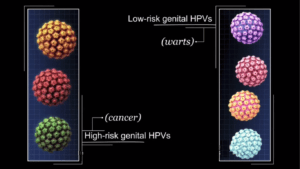
High-risk wart causing cancers vs Low-risk warts of genital HPV
Some genital HPVs are high risk, they can lead to cancer of the lower end of a woman’s uterus called the cervix. Commonly this HPV s can lead to other genital-anal or oral cancers in both women and men. It’s important to know that most HPV infections caused no symptoms.The low-risk genital HPVs that cause warts are not an important cause of cancer.People infected with either a high-risk or a low-risk genital HPV, spread it through skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal or oral sex for infection.
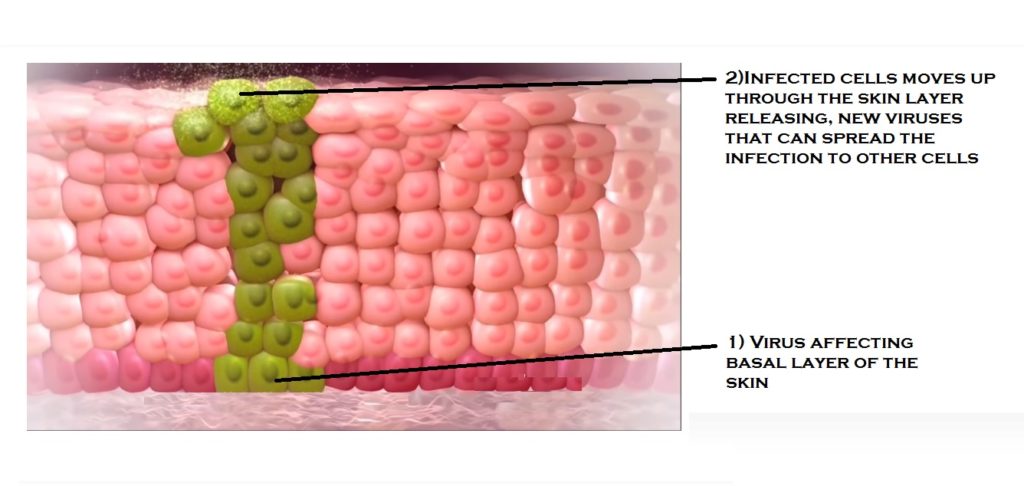
HPV enters through tiny cuts in the skin around or inside the penis, vagina, throat or anus. The virus makes its way down to the cells in the bottom or basal layer of skin. They infect them, as the infected cells divide the virus. It begins to make copies of itself. Eventually, the infected cells, move up through the skin layers. It releases the new viruses that can spread the infection to other cells.
For most people, the cells of the immune system can destroy the infected cells along with the virus within 2 years. 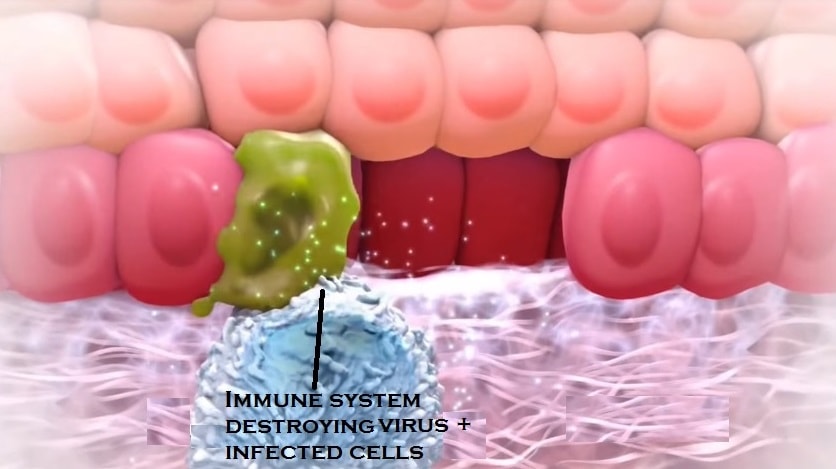 But in some
But in some
, the immune system isn’t able to destroy all of the viruses leading to an infection that doesn’t go away. HPV infected cells may multiply over several weeks or months.
If the cells are infected with low-risk HPV they begin to form warts around the genitals. If the HPV is high-risk it may damage the cells genetic material causing the cells to become pre-cancerous over a period of years. A cancerous tumor may slowly form as the damaged cells continue to multiply.
HPV vaccine to protect against cancer
- It is suggested to get tested for cervical cancer, routine screening for women aged 21 to 65 years old can prevent cervical cancer.
- If boys and girls miss the vaccine given in preteen age, Catch up test is recommended for the boys and men through age 21 and for girls and women through age 26.
- Gay and Bisexual men are suggested to get tested at around age 26 years.
The most common cancer from high-risk genital HPV is cervical cancer. There is no cure for any type of HPV infection.However, the Gardasil vaccine can help protect against two of the most common high-risk HPV s that cause genital
cancers. The vaccine also helps protect against two of the most common low-risk HPV s that cause genital warts.
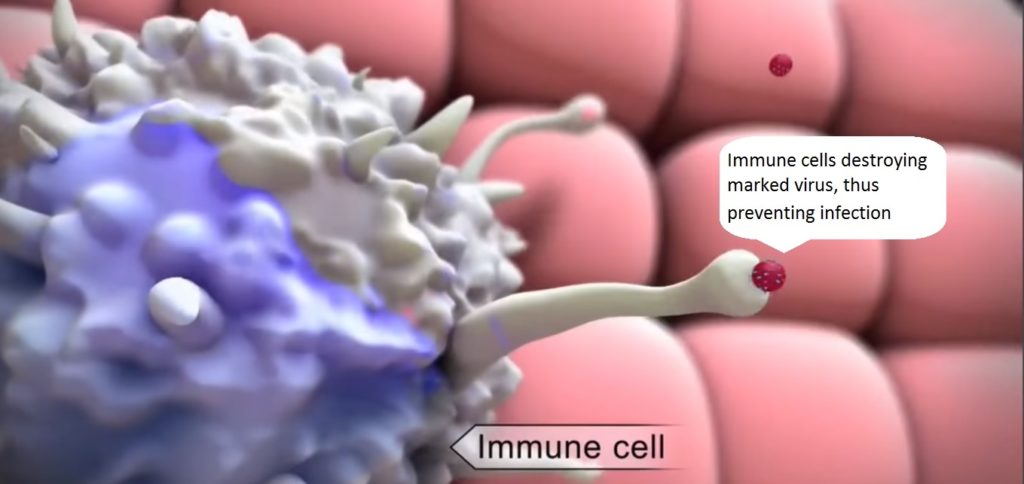
For best protection, CDC suggests that preteen girls and boys(11-12 years) should receive three doses of the vaccine over a period of six months. Before any sexual activity takes place. The vaccine injects dead proteins from HPV viruses into the bloodstream. These proteins don’t cause infection but the proteins do stimulate certain immune cells to create markers called antibodies. This can identify these HPV s. Later if the live versions of these viruses invade the skin, the antibodies recognize and attach to them these immune cells destroy the marked viruses which prevent an infection from happening.
It is important to note that the vaccine does not protect against other types of HPV. The vaccine also doesn’t reliably treat cells that are already infected. High-risk genital HPV that cause cervical cancer is most treatable when diagnosed early.
Pap Test
Women should have a Pap test to see if their cervix has abnormal or precancerous cells. Even if they’ve had an HPV vaccine check with a health care provider to find out how often to get this test during this procedure.
A healthcare provider will collect a small sample of cells from the cervix, these cells will be examined under a microscope to see if they’re abnormal or cancerous. A separate HPV test will look for genetic material from high-risk types of HPV when a Pap test and HPV test are done together it’s called Co-testing.
If the above tests show abnormal cells. A healthcare provider will recommend specific treatment based on the woman’s age, medical history and the abnormality of her cells. While there is no cure for an HPV infection both abnormal and cancerous cells can be treated.
Females who get routine Pap tests and follow up as needed can identify problems before cancer develops.
Save $10 on STD testing using this link
Treatment of HPV
Some types of HPV can cause common skin warts or genital warts may go away without treatment as the immune system fights off the HPV infection if the warts are painful or don’t go away visit a healthcare provider. So they can examine warts to determine.
The best way to remove them (although you can treat common warts at home) do not treat genital warts yourself procedures to remove either common warts or genital warts include freezing with cryotherapy burning with an electric current called
electrocautery.
Surgical removal for more information talk to a healthcare professional can also be considered.
Summary
- Cervical cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among women.
- High-risk HPV is a necessary cause of cervical cancer
- 80% of women will spontaneously clear HPV virus in 2 years
- Only 3-10% of women with High-risk HPV will develop precursor cancer lesion
- High-risk HPV screening has high NPV(Negative predictive value), but low PPV (Positive predictive value)
- More specific tests are needed if tested positive
2.Trichomoniasis causing Cancer
‘Trichomonas vaginalis’ is responsible for a sexually transmitted infection known as trichomoniasis the symptoms mainly occur in women in the vagina. This STD is not caused by a bacterium but rather a protozoan which is a more advanced form of microorganism than a bacterium. This protozoan specifically is a parasite and it exists mainly by eating cells that they destroy, so eating cell fragments. This protozoan uses these cell fragments or these pieces of cells for its nourishment.
At the cervix, long-term inflammation due to can cause irregularities in cell formation or cell division at the cervix over time producing cervical cancer. The idea though is that because women tend to have symptoms we will catch the trichomonas earlier on and treat them.
The study from other institutes like NCBI govt institute from China and University of California too confirmed the relationship. After they carried out a research on cervical cancer and found that there is a relationship between Trichomonas vaginalis infection and cervical cancer.
Private STD testing: Discreet without compromising on the privacy
About trichomoniasis disease
This disease spreads mainly or only through vaginal sex and what makes this infection very interesting is that the trick ammonia protozoan can’t survive anywhere else so they can only live within the urogenital tract. Now if you think Trichomonas vaginalis live within women like in the vaginal tract or in the urethra but not in men? You are wrong Trichomonas vaginalis infects men or enter men’s body too but the tricky thing about that with men is that they rarely have symptoms. So they’re asymptomatic which means that they’re carriers of this infection, so they’re asymptomatic carriers that can spread this STI
to women without even realizing it.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8520717
https://health.ucsd.edu/news/releases/Pages/2016-01-27-NCIs-unanimous-statement-HPV-vaccination.aspx


