Sensitivity and Specificity both influence, how valid or in other words how accurate a clinical test is. Validity means to what degree a test measures what it claimed to measure. The concepts of sensitivity and specificity will tell you which tests you should use to confirm or exclude a hypothesis.
If the outcome of a test is reported dichotomously (ie, positive or negative), its performance characteristics can be expressed in at least 2 ways. 1)Sensitivity and Specificity 2) Positive and Negative predictive value. Clinically, these concepts are important for confirming or excluding disease during the screening. So let’s take a look at each of these parameters.
Sensitivity in Screening
Definition: Sensitivity is the ability of a test to identify patients that have the disease.
So if 10 people have a disease and eight of ten of those patients as being positive. Then those are true positives. Sensitivity then is 80%. Rest two of those patients, however, are going to be negative, even though they have the disease and those are called false negatives.
So when a test that is highly sensitive is good for ruling out disease, when the test is negative (test result)
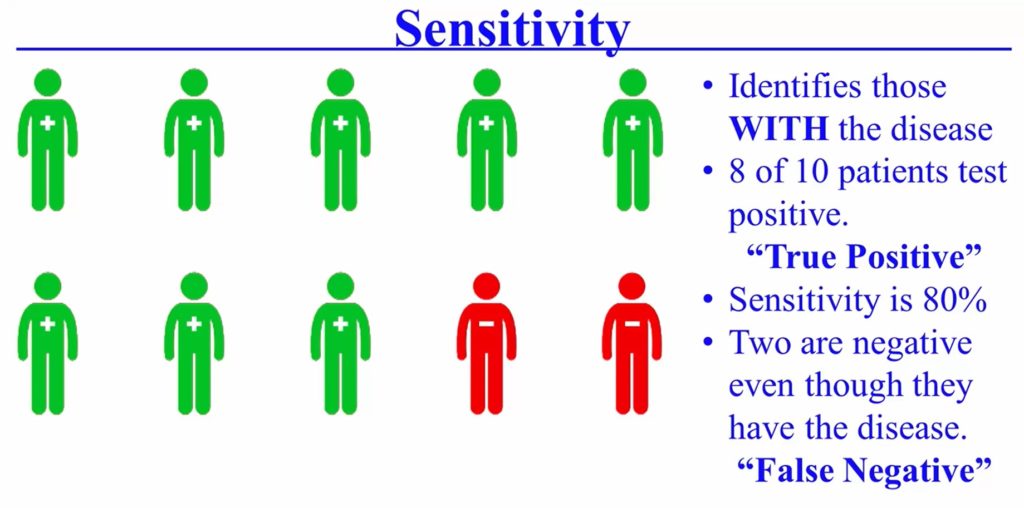
Example: So if I have a test that is let’s say it’s 95 percent sensitive if that test is negative I know with the 95 percent assurance that I’ve ruled out that disease.
The factor ‘Sensitivity’ in a test is used as a preliminary screening tool, as it just detects the problem and doesn’t necessarily indicate one. So when a test with a high sensitivity test comes positive, it is recommended to do another test which will pin-point or will be with more specificity which will be explained after this. Also, sensitivity doesn’t address the prevalence of the disease, so it doesn’t matter how the prevalence of a particular disease in the population, sensitivity is independent of it.
That brings us to the second term specificity.
Specificity in Screening
Definition: Specificity of the test, is its ability to identify those without the disease.
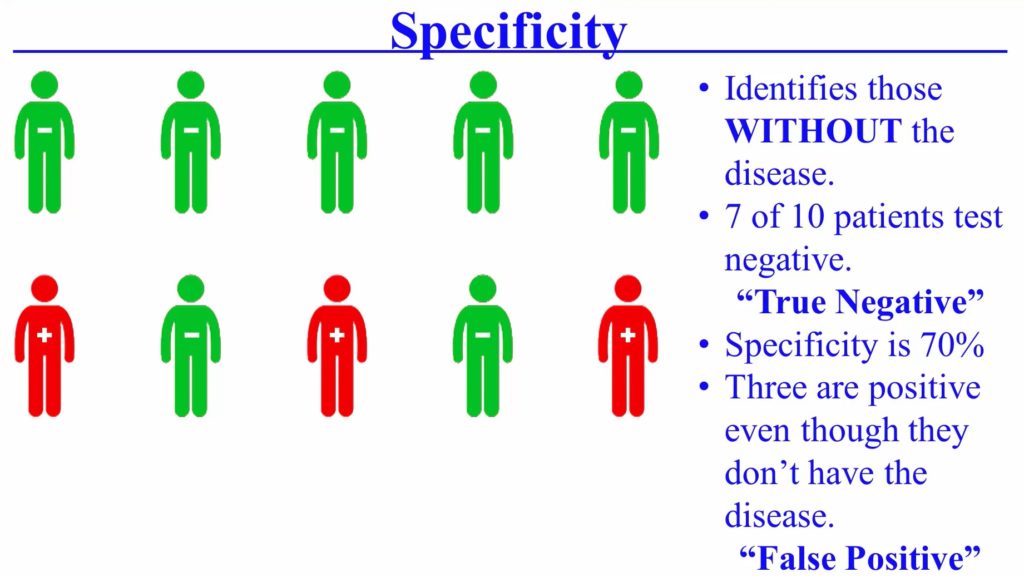
10 people don’t have any disease. So if 7 out of 10 patients have been tested negative because they don’t have the disease and it didn’t show in the test as well. So those are truly negative and the Specificity of the test is 70%. So, 3 of them have been indicated as positive, even though they don’t have the disease. Those are referred to as False positive.
So when the test is specific is good at ruling in the disease when test positive
Just like sensitivity, specificity is not related to the prevalence of the disease
Calculation of Specificity and Sensitivity in a test
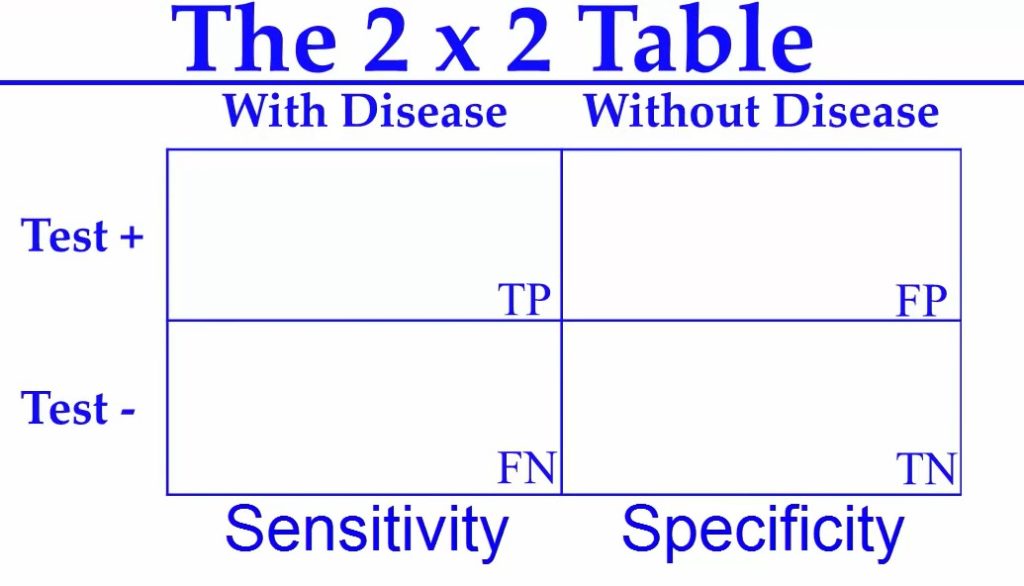
In the above table, we have patients with the disease and we have patients without the disease. We’ll say that this left column has to do with Sensitivity and the right column has to do with Specificity. The top row is the test is positive, so everybody on the top row is positive everybody. On the bottom row, the test is negative.
So now let’s talk about sensitivity (entire left column).
We found that we had 8 patients tested positive and those were true positive(TP). We found out that we had 2 patients test negative(TN), but they were false negatives.
So the formula is Sn = TP/(TP+FN) TP:True positive; FN: False Negative
The formula is to divide the true positives by the true positives plus the false negatives, in other words, everybody the population and in this example, the sensitivity turns out to be 0.8 or 80%. How? Using above formula Sn= 80/(80+20) ; Sn =0.8 or 80%.
Specificity Calculation
Now let’s calculate specificity in our example. We had 7 people who were truly negative and we had 3 people with false positives.
So, according to the formula: Sp= TN/(TN+FP); TN:True Negative, FP: False Positive
Specificity=7/(7+0.3); Sp: 0.7 or 70%.
Positive Predictive Value (PPV)
Positive predictive value is the ability to detect the presence of disease.
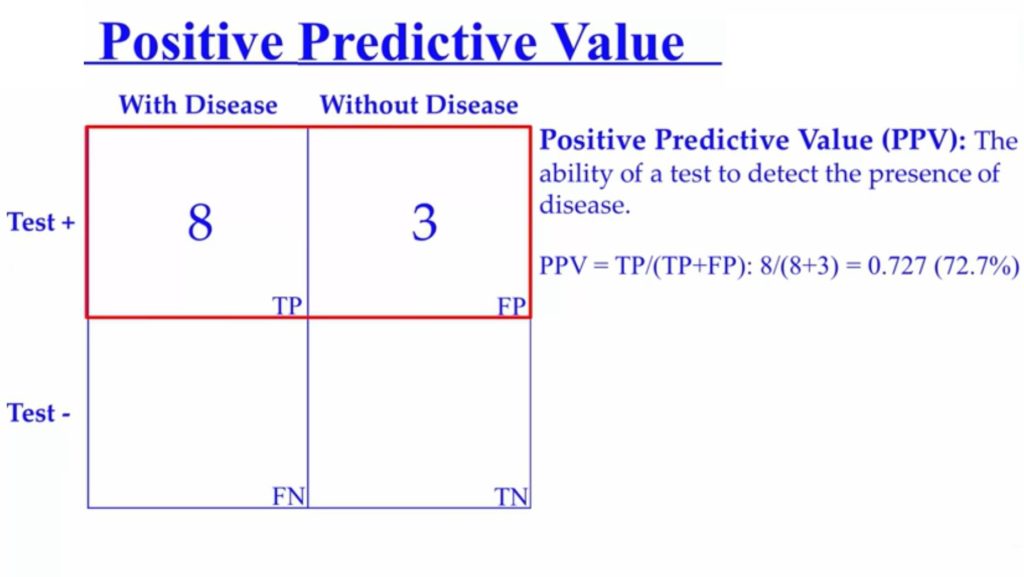
It measures the probability of having the disease when the test is positive. so in our example, 8 people tested positive for the disease and that they had the disease, so true positives(TP). 3 people tested positive for having the disease but they didn’t have it. So those were false positives(FP).
Our formula is to divide the true positives by the true positive plus the false positives and in this case, the positive predictive value is PPV= TP(TP+FP)
PPV= 8/(8+3); 0.727 or 72%
and again is the probability that the patient has the disease when the test is positive.
Negative Predictive Value (PPV)
Negative predictive value is the probability of not having the disease when the test is negative.
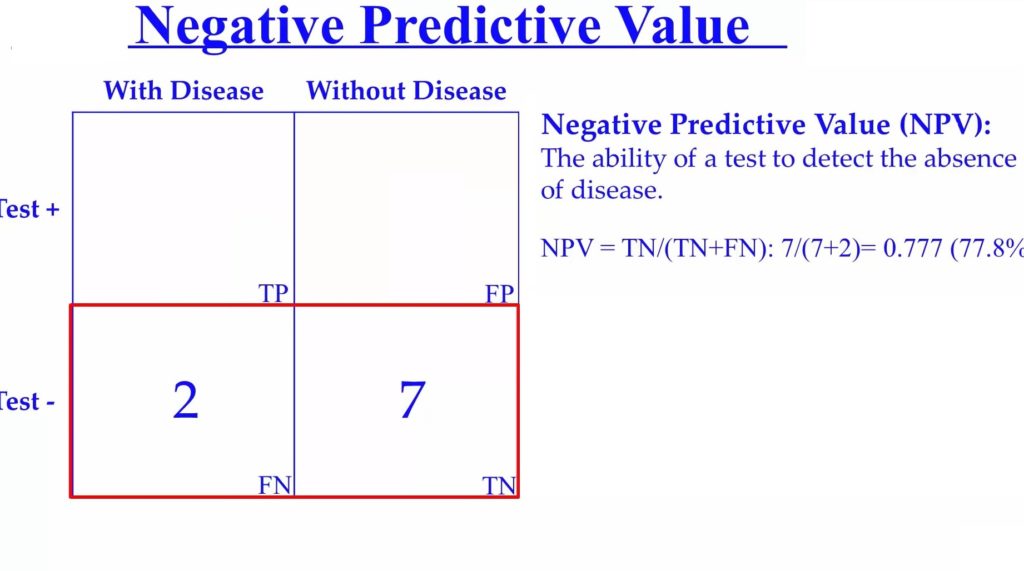
In our example, we had 2 people with false negatives(FN) and we had 7 people with true negatives (TN). Our formula here is to divide the true negatives by the true negatives plus the false negatives.
NPV= TN/(TN+FN): 7/(7+2); = 0.778
or giving us a negative predictive value of 77.8%.
Bottom line
As seen from the above examples high Specificity, Sensitivity and Predictive value don’t guarantee an accurate diagnosis. Too much or too little Sensitivity or Specificity in the diagnosis can lead to False positive or negative test results. What is really important is to have the balance of all so that we can avoid False(+ – ) test results. Thus, everything ultimately lies with a good and experienced diagnosis partner. At STDcheck.com they claim to maintain the optimum level of testing parameters inside their HIPAA compliant labs, thus resulting in highly accurate test results. With more than 15 years in the business and with +4500 STD testing center STDcheck.com is a reputed name in the STD diagnosis domain.
Get Tested Now and avail up to $10 discount using this Exclusive link


