Being in a new relationship? Know the safe time gap between two consecutive sexual encounters.
From the research, it can be concluded that the safest gap between two consecutive sexual relationship is 90 days for men and 120 days for women. Although there are several other factors impacting the safety.
New relationships bring much more than love in the life of individuals. It brings new hope, newly felt happiness, new trust & belief in your partner. These are all positive aspects of love and being in a newly formed relationship, the one people are happy and content with.
What about some negative physical or health conditions brought from the past relationship?. A Sexual health condition from the past relationship or any untreated sexual disease your partner might be carrying from the past.
How often do couples consider getting tested for STD in a relationship?
Ideally, a sexually active couple should get tested for STD anywhere between 3-6 month. Best way is of course to get tested for STDs and HIV at the testing center near you. But this does not happen during the initial phase of the relationship. Non detection of STI leads to spread of STIs, especially when most of the STDs are asymptomatic in the initial phase. It has been noticed that couples in newly formed relationships engage in sexual activities before thinking about getting tested.
Most couples only opt for STD/STI testing either when they observe an STD symptom or after they have decided to be in a serious long term relationship. Moreover, an initial casual relationship might not be monogamous and may involve multiple partners before getting into a serious one.
This gives rise to a million dollar question…
What should be the gap between Consecutive Sexual Partnerships to avoid STD/STI?
There has been an experiment conducted in Russia to precisely know the safest time gap between two consecutive sexual relationships. This is the question which comes to almost every mind entering into a newly formed relationship.
The subjects were categorized into 4 categories as per their time gap between past and newly formed relationships. So the categories were as follows
- Overlapping (0 or negative gap or double dating)
- Short gaps (1–90 days)
- Mid-length gaps (91–365 days)
- Long gaps (366 days or more)
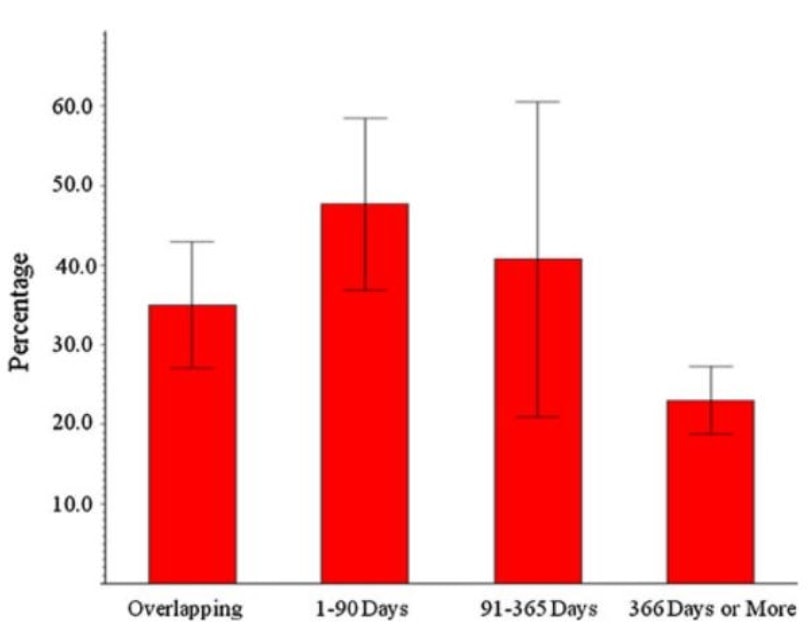
Following is the result of the experiment
Important factors to consider here.
The likelihood that someone will transmit or gets contract by STD depends on the following factors
- Characteristic of the STI’s infection agent
- Behavioral characteristics of the partners exposed to infection
- Type of sexual behaviour (Straight/ Gay etc)
The percentages of STIs among the participants with overlapping relationships is 35.0, mid-length is 47.7, long gaps is 40.7 and super long gap is 23.0%, respectively (refer above figure) Compared to participants with long relationship gaps, the percentage of STDs & HIV was significantly higher among those with overlapping relationships (q-statistic = 3.8, P < 0.05) and short relationship gaps (q-statistic = 6.2, P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between the STD prevalence of participants and medium relationship gaps and other gap lengths.
Although concurrent sexual partnerships are the most vulnerable group for STIs, such as HIV contraction, the length of time between two consecutive sexual partnerships for monogamous individuals (referred to as the “gap”) is also an important factor.
other observation of the research…
People with Overlapping or multiple partners are at 35% of risk of contracting STD. As the gap progresses the chances of contracting STD increases up to 90 days. Beyond 90 days gap, (gap between consecutive sexual encounters) it has been observed that chances of contracting STD starts reducing.
Bottom line
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that short gaps between relationships, rather than concurrent partnerships were associated with STDs when contrasted against long term gaps for this sample of STD clinic patients. As the time gap between 2 sexual partnership increases, the chances of contracting or acquiring STD/STI decreases drastically.
Thus we can conclude that the risk of a sexually transmitted infection (STI) significantly decreases for serially monogamous individuals when the time between partners increases to longer gaps than 3 months for men and for female it is slightly longer, it is 4 month, according to a study.
“
References
Experiment to know the relation between STI and gap between sexual partnership conducted in russia: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3157580/