What is Seroconversion of HIV?
Seroconversion in HIV is the period during which the body starts producing detectable levels of HIV antibodies. After exposure to the HIV virus, the body’s defense mechanism comes into action. Thus, the immune system begins to develop antibodies to attack the virus. This production phase of detectable levels of HIV antibodies is called seroconversion.
So the Seroconversion is the phase when the tests (HIV tests based on antibodies) can actually detect the presence of the HIV virus in the body. This is the stage after which the HIV virus starts affecting the immune system(by depleting it) of the body and rapidly replicate itself.
Why is it important to tap the Seroconversion timeline?
It is important to know the Seroconversion timeline from the time of exposure, to get a correct and timely diagnosis for HIV. As timely diagnosis could lead to timely treatment of HIV, it is essential to have a track of the Seroconversion timeline.
There are certain factors cause Seroconversion delay which includes the use of PEP, this will be discussed later.
To prevent the spread of HIV to others during Seroconversion. This is another reason why it is important to gauge the Seroconversion on time, as the time between exposure and the immune system’s initial response is a period of “ acute HIV infection”. This is because the body is yet to produce a higher amount of antibodies and thus, the viral level in the body is extremely high.
HIV Seroconversion timeline
Thus referring to the fig. following things can be observed
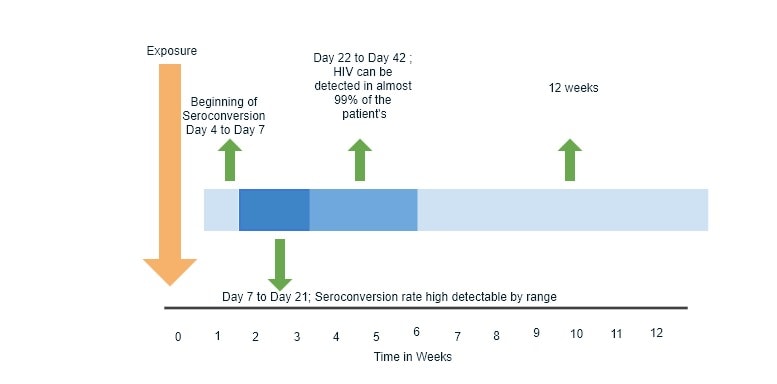
Seroconversion: Although it begins in 4-5 days from the time of exposure, the detectable range Average timeframe (for entire seroconversion): 7-21 days; 95% people by 4 weeks.
- HIV RNA test (viral load): Detection span: average 7-14 days since exposure
95% people: 7 days-6 weeks.
HIV RNA (Viral load) test is sensitive 3 days before seroconversion symptoms. Thus, it is the best option in the timely detection of HIV virus.
- P24 test: The p24 antigen assay measures the viral capsid (core) p24 protein in blood that is detectable earlier than HIV antibody during acute infection
Detection span: Avg. 16 days; 95% of people from 1-8 weeks, then reduce to very low levels.
P24 is used to confirm the presence or absence of the virus after an HIV RNA test.
- Seroconversion after 8 weeks: On Average, this is probably the ideal time until the Seroconversion phase lasts. In 95% of the cases (graph changes), 7-8 weeks is the maximum period of Seroconversion.Seroconversion after 12 weeks: This delay in seroconversion happens due to delayed Seroconversion. The delay in Seroconversion phase may happen due to any particular reason mentioned below including:
- Immune system: The immune system differs from person to person. So, the human body producing antibodies (detectable levels) will also differ.
- The maximum period of Seroconversion: There are instances when the Seroconversion periods have lasted as long as 24 months. But on average, for nearly 95% of the people infected, the seroconversion period is 12 weeks.
Symptoms of HIV Seroconversion
The most common symptoms during HIV seroconversion period could include the combination of the following
- Flu-like symptoms
- Fever
- HIV rash
- Sore throat, swollen lymph nodes
Cases of delayed in HIV Seroconversion
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (or PrEP) is used when people at risk for HIV take daily medicine to prevent HIV. PrEP can stop HIV from taking hold and spreading throughout your body. But a recent study revealed that people on PrEP who get infected may have a delay in the detection of HIV infection.
In a study conducted on several patients with early-stage HIV (HIV-1). It was observed that the PrEP delayed the time to detect seroconversion for those participants who continued to take PrEP during acute/early clade C HIV-1 infection.
Thus, the ongoing PrEP use in seroconverters may delay the detection of infection and elongate seroconversion, although the delay does not increase the risk of resistance.
HIV seroconversion and False-negative testing
a) If the body hasn’t started to create antibodies against HIV, there is a chance that even an HIV test, checking for antibodies will detect negative.
Thus, the case with the PRep test discussed above.
b) Also, before seroconversion, there may not be detectable levels of HIV antibodies in a person’s blood. Thus, giving a false-negative test result.
c) The facts are that, after exposure within about 15 days, in fact, it could be earlier but definitely by day 15, if you do an RNA PCR test and it comes back negative the chances that you’re infected are extremely low.
Get tested for HIV RNA test with $10 discount coupon. Click here !!
d) By the end of 6th weeks after exposure, it could be sooner as soon as three to four weeks if a 4th generation antigen-antibody test is conducted and is negative you can almost be sure that HIV infection has not occurred and by all protocols.
Get tested for HIV 4th generation HIV 1 & 2 Antibody test with $10 discount coupon. Click here !!
Reference
nejm.org
How Does PrEP Affect Seroconversion After HIV is Acquired?: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5578893/


